PRENUMERERA & SPARA 20%
FRI FRAKT
Kommer du ihåg ditt lösenord?
Subscribe to receive a guaranteed shipment of formula every month.
Enjoy a {{ discount_amount }} discount on product throughout your subscription.
Change or cancel your subscription at any time!


Välj ett solskydd som skyddar mot både UVA- och UVB-strålning som har ett högt till mycket högt skydd, dvs SPF 30–50+. Solskydd som även ger ett bra skydd mot UVA-strålning har en UVA-symbol (bokstäverna UVA i en rund ring) på förpackningen. Utöver detta rekommenderar vi att man väljer ett fotostabilt solskydd vilket innebär att det inte tappar effekt när du befinner dig i solen (läs mer om fotostabila solskyddsfilter här).
Gör din hud en tjänst genom att välja en produkt som inte innehåller parfym. Många parfymer är allergiframkallande ämnen och dess effekter kan intensifieras när de utsätts för direkt solljus.



För att få rätt skydd från solens skadliga UV-strålar är det bra att hålla koll på UV-indexet i ens område – beroende på vilken nivå det är på kan man välja ett högre eller lägre solskydd. UV-indexet är en internationell standard som används för att mäta hur intensiva (dvs skadliga) UV-strålarna är på en angiven plats och vid en viss tidpunkt. Nedan bild visar hur UV-index normalt är i Sverige.
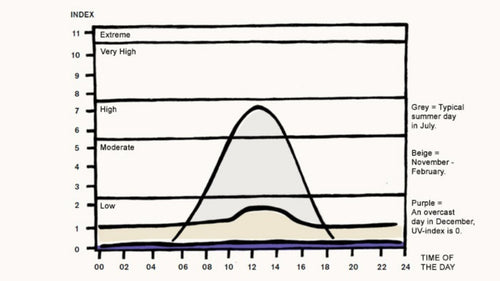

Bild 1. UV-indexets variation med årstid, väderlek och tid på dygnet, ju högre indexvärde desto starkare är UV-strålningen du utsätts för.
Under sommarsäsongen är UV-index i skandinaviska länder vanligtvis mellan 4–7 och under vintern lägre än 2. Vid ett lågt UV-index (under 2) behöver man inte använda solskyddsmedel, men vid ett högre UV-index (mellan 4–7) ökar riskerna för negativa effekter av strålningen och då måste du skydda dig.
En allmän rekommendation är att använda ett högt till mycket högt solskydd (SPF 30-50+) dagligen om man vistas utomhus under sommarhalvåret (slutet av mars-oktober) eftersom UV-index är som högst under denna tid.
Gör vårt solskyddstest här för mer info om val av solskydd.
För att få det skydd som utlovas på förpackningen måste du applicera solskyddet i ett jämntoch tjocktlager och även återapplicera med jämna mellanrum, särskilt om du har badat eller tränat. Hur ofta det behövs beror på hur aktiv du är och hur mycket produkten gnuggas av, men som regel är det är bra att återapplicera varannan timme och speciellt efter att du badat. Nedan är vår rekommendation om hur mycket du behöver applicera för ansikte och kropp.
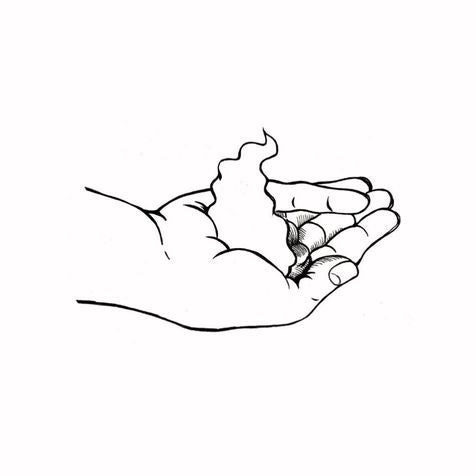
För att vara säker på att man får det skydd som står på förpackningen så gäller det att applicera mer än vad du normalt sett gör. Så mycket som 30-40 ml bör man applicera på kroppen för att få ett fullgott skydd. Och hur mycket är 30-40 ml? Det är ungefär lika mycket kräm som får plats i din kupade hand.
När det gäller ansiktet så är det över 1-2ml solskyddsprodukt som gäller. De allra flesta av oss tar för lite solskydd för ansiktet så tänk på att du behöver ta betydligt mycket mer än vad som kanske känns lagom för att få den skyddande effekten. Så smörj på ordentligt, hellre för mycket än för lite!


Det som skyddar i en solkräm är olika typer av filter som brukar delas in i organiska (kemiska) och mineral (fysikaliska) filter. Många använder organiska filter eftersom de ger en skönare och bättre produkt att smörja in, de ger nämligen inte den vita lite kladdiga hinnan på huden som produkter med höga halter mineralfilter kan ge.
Från ett hudperspektiv kan mineralfiltren titandioxid och zinkoxid vara att föredra eftersom de inte penetrerar (tar sig igenom) huden. Därför är kroppen mindre benägen att reagera på mineralfilter. Det är bl.a. den låga risken för allergier som gör att mineral filter ofta används för barn och personer med känslig hud. Den kosmetiska effekten kan dock upplevas som bekymmersam då mineralfilter kan ge en vit hinna på huden.
De nya och mest moderna organiska filtren består dock av större molekyler som även de har mycket låg benägenhet att penetrera huden. För dessa ämnen har fördelarna med de organiska filtren och mineralfiltren kombinerats, d v s de ger en skön produkt att smörja in samtidigt som de är så pass stora att de stannar på utsidan av vår hud. Vår uppfattning är därför att den bästa solskyddsprodukten, som ger bäst skydd och bäst produkt att smörja in, är den som innehåller en kombination av moderna organiska filter och mineralfiltren zinkoxid och titandioxid.
Bland de organiska filtren anser vi att man bör undvika ämnena från den äldre generationen, de som har en mindre molekylstorlek och som kan penetrera huden. Den äldre generationen filter har en större benägenhet att orsaka allergier och hudproblem, man har även i vissa fall uppmätt halter av dem i urinen, vilket visar på ett upptag och sett hormonstörande effekter. De har även i många fall visats ha en negativ påverkan på miljön.
Om du vill veta vad som är vad kan du titta efter följande i INCI-listan på produkten:
Exempel på nya moderna organiska UV-filter (INCI) som vi rekommenderar: Bis-Ethylhexyoxyphenol Methoxyphenyl Triazine, Diethylamino Hydroxybenzoyl Hexyl Benzoate, Diethylhexyl Butamido Triazone, Ethylhexyl Triazone, Tris Biphenyl Triazine, Ethylene-bis-benzotriazolyl tetramethylbutylphenol Disodium Phenyl Dibenzimidazole Tetrasulfonate.
Namn på den äldre generationen organiska UV-filter (INCI) som bör undvikas: Benzophenone-3, Ethylhexyl Methoxycinnamate, Homosalate, Ethylhexyl Salicylate, Octocrylene, Butyl Methoxydibenzoylmethane, Phenylbenzimidazole Sulfonic Acid, 4-Methylbenzylidene Camphor, Ethylhexyl Dimethyl PABA
Mineral filter i solskydd som vi rekommenderar (INCI): Titandioxid, zinkoxid
Vårt tips är även att välja solskyddsprodukter från europeiska företag utvecklade för den europeiska marknaden, då de oftare använder nyare varianter av UV-filter som är bättre från ett hud- och hälsoperspektiv. FDA, som reglerar användningen av UV-filter i USA, har än så länge inte godkänt flera av de europeiska varianterna och amerikanska företag tenderar därför att fortfarande använda de äldre filtren. Är du intresserad av olika UV-filters miljöpåverkan kan du läsa mer här.


Kläder är den första försvarslinjen mot solen. Hur påverkar olika klädesplagg hur väl du är skyddad? Här är några grundregler:
Mörka kläder: Svart och marinblått, absorberar mer UV-strålar än ljusare färger som vitt och pastellfärger. Till exempel ger en vanlig vit t-shirt i bomull en SPF på endast ca 10.
Som en tumregel - ju mer intensiv nyansen är, desto bättre skydd kommer kläderna att ge.
Material: Precis som färg kan material och struktur på dina kläder påverka hur väl de skyddar dig mot UV-strålar. Syntetiska och halvsyntetiska fibrer som polyester eller rayon är de bästa valen för solskydd, liksom täta, tunga, tätt vävda tyger som ull, denim eller manchester. I motsatta änden av spektrumet finns lätta tyger (till exempel raffinerad bomull), som tenderar att vara tunnare och låter därmed mer ljus passera igenom. Exempel:
Storlek: Det är ganska uppenbart att ju mer hud du täcker, desto bättre skyddas du. Det kan vara lätt att glömma att samma sak gäller hattar! De bästa hattarna för solskydd har en bred kant (3 tum eller mer). Glöm inte att använda solglasögon och använd gärna ett par robusta solglasögon med breda glas som täcker ögonen, ögonlocken och så mycket av de omgivande områdena som möjligt.
Lös passform: En skjorta med lös passform ger bättre SPF än en tight.